Compliance best practices checklist for support coordination and managers
When Compliance Needs to Be Completed in NDIS
In NDIS Support Coordination, compliance must be completed at the beginning, during, and after support delivery to ensure all participant records and risk management obligations are met under the NDIS Practice Standards (especially the Core Module – Rights and Responsibilities, Provision of Supports, and Governance and Operational Management).
Key compliance checkpoints:
- Initial Onboarding – Before any supports are delivered, participants must have:
- A Support Plan that details their goals, needs, and service arrangements.
- A Vulnerability and Risk Assessment to identify potential risks to the participant or others.
- An Emergency Plan outlining what to do in case of health or safety incidents.
- During Service Delivery – Compliance must be reviewed regularly to ensure:
- Supports align with the participant’s current NDIS plan and goals.
- Any changes in health, environment, or risk are captured and updated.
- Records in systems like Careflo and Compliance Tracker stay current.
- After or at Review Time – Before the participant’s plan review or service renewal:
- All documentation must be finalised, uploaded, and auditable.
- Evidence of communication, consent, and risk management must be verified.
Completing compliance at these points ensures that the participant’s wellbeing, safety, and funding integrity are protected and that your organisation meets NDIS Quality and Safeguards Commission standards.
Why Support Plans, Emergency Plans, and Risk Assessments Matter
1. Support Plans
These are the backbone of the participant’s journey.
They:
- Translate participant information into actionable steps for support coordinators and service providers.
- Serve as the key compliance document during NDIS audits (evidence of planning and coordination).
Without an up-to-date Support Plan, your team risks:
- Delivering supports that aren’t aligned with the participants needs.
- Breaching the Provision of Supports Practice Standard.
- Missing opportunities to review outcomes and adjust supports effectively.
2. Emergency Plans
Emergency Plans are mandatory for all participants.
They:
- Document what to do in case of medical, environmental, or behavioural emergencies.
- Provide clear escalation pathways (who to call, what actions to take).
- Ensure duty of care during an emergency.
NDIS auditors expect that emergency plans are personalised, tested for clarity, and accessible to anyone delivering support.
3. Vulnerability and Risk Assessments
Risk Assessments protect both the participant and the organisation.
They:
- Identify potential risks in the participant’s home, environment, or from their supports.
- Establish mitigation actions (e.g., training, environment changes, support ratios).
- Demonstrate proactive management — a key indicator of quality and safety compliance.
The NDIS Commission explicitly requires providers to “identify and manage risks associated with the provision of supports,” which makes risk assessments a non-negotiable part of compliance.
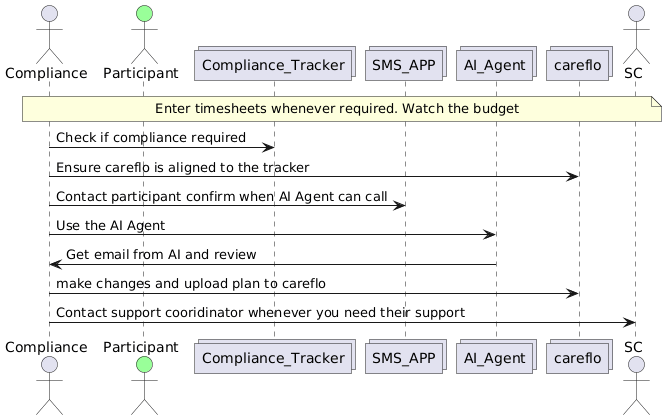
How It All Fits Together (as shown in your diagram)
The diagram flow shows the compliance ecosystem:
- Compliance Tracker ensures that no compliance item is missed or overdue.
- Careflo acts as the single source of truth for participant records.
- SMS App and AI Agent coordinate communication and automate plan updates.
- Support Coordinators (SC) are looped in whenever human input or validation is needed.
This process ensures compliance is:
- Timely – completed before supports are delivered.
- Consistent – all plans and documents align across systems.
- Auditable – every action is tracked, traceable, and reviewable.